CrO4- + H+ gives Cr2O72- + H2O
So option ii correct
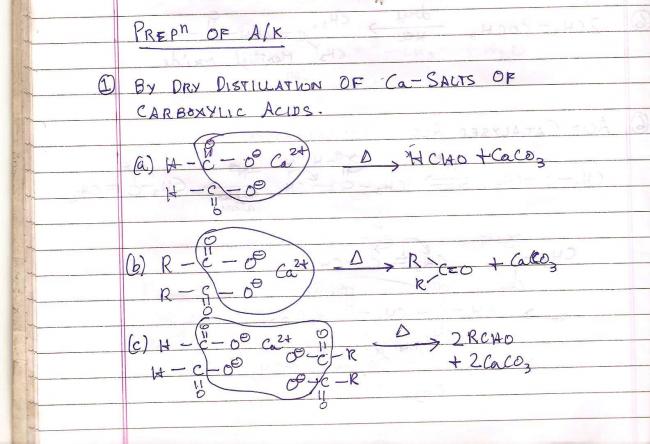
Heating a mixture of calcium formate and calcium acetate produces
acetone
acetaldehyde
methane
formaldehyde
BaO2 + H2SO4 ---> BaSO4 + H2O?
Ek toh -2 hoga...dunno about BaSO4.
The number of moles of KMnO4 that will be needed to react completely with one mole of ferrous oxalate in acidic solution is
3/5
2/5
4/5
1
The oxidation states of the most electronegative element in the products of the reaction , BaO2 with dil. H2SO4
0 and -1
-1 and -2
-2 and 0
-2 and -1
Shreyan that's just one calcium salt.... You must have seen my image...thats how they form.
The (b) option corresponds to the calcium salt you are referring to(for producing acetone).
Actually the end product has to have calcium carbonate. I suppose that's why..
Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by SN2 mechanism because of
insolubility
instability
inductive effect
steric hindrance
@ Pritish: one doubt....are u sure that heating of calcium formate will produce HCHO? the mechanism i read (for calcium acetate) was this: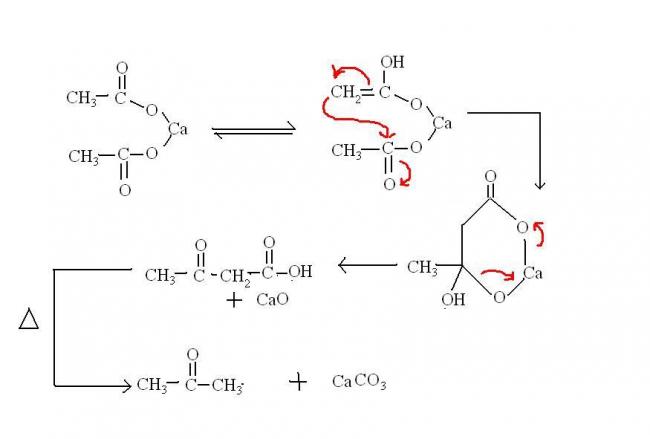
How can HCHO form using this mech?
What would happen when a solution of potassium chromate is treated with an excess of dilute nitric acid?
Cr3+ and Cr2O72- are formed
Cr2O72- and H2O are formed
CrO42- is reduced to +3 state of Cr
CrO42- is oxidised to +7 state of Cr
Compare the stability of their conjugate bases.
I - CO32-
II - H2O
III - SO42-
IV - SO3F-
The stablest out of these is II as it has no formal charge. Next in line is IV as it is stabilised by -I effect of fluorine.
Now the battle is between carbonate and sulfate anions. You may recall that sulfuric acid and carbonic acid both have two acid dissociation constants, of which for sulfuric acid the second one is small. It is not so for carbonic acid.
Hence I is more stable than III.
So the order of stability of conjugate bases is
II > IV > I > III
In the same order follows their acid strength (the acid with the most stable conjugate base is most likely to lose a proton) -:
II > IV > I > III
Four species are listed below
(i) HCO3- (ii) H3O+ (iii) HSO4- (iv) HSO3F
Which of the following is the correct sequenece of their acid strength?
iii < i < iv < ii
iv < ii < iii < i
ii < iii < i < iv
i < iii < ii < iv
Ans i < iii < ii < iv
This is a method of preparation of aldehydes and ketones. It is by dry distillation of calcium salts of carboxylic acids.
Ca(HCOO)2 + Ca(CH3COO)2 ----> 2CH3CHO + 2CaCO3