y don't u jst gv link 4m whr u r coping nd pastingit..............tht wld be much easier[9][9]
DAVISSON-GERMER EXPERIMENT
Davisson and Germer realized an experiment where it can be observed the “wave like†behavior of the electrons. They could verify experimentally the De Broglie formula for the electrons.
The Davisson-Germer apparatus is a vacuum glass tube which has in its interior an accelerator of electrons, a known crystal structured substance as target and an electron detector.
Next is a simplified schema of the experiment:
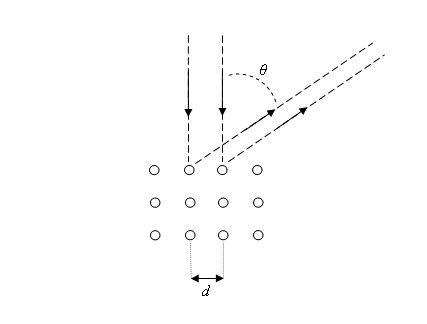
The accelerator is composed of two plates with terminals outside for connecting to an external voltage and with a hole in a plate to form a beam of electrons with certain velocity. The crystal target is where the electron beam collides and is diffracted. The electron detector can rotate around the target to detect in what directions the beam of electrons is diffracted.
The experiment showed that the electrons satisfied the relation for constructive interference:
dsinθ = nλ
A beam of diffracted electrons is observed for the angle that satisfies the relation above for the De Broglie λ of the electrons:
λ = h/mv
Davisson and Germer used a formula that is delivered from the calculation of the velocity v of the electrons as a function of the known value of the potential V through the accelerating plates that is valid for slow velocity electrons as we see next.
The Kinetic Energy reached by the electrons equals the Potential through the plates:
Ec = ½ mv2 = eV
and from the De Broglie formula we have:
λ = h/(2emV)1/2
where e and m are the charge and the mass of the electron.
This value of λ is used in the experiment and verifies the constructive interference relation.
-
UP 0 DOWN 0 0 2
