 4
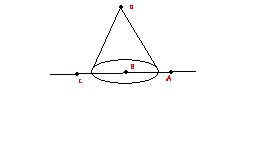
42) A right circular imaginary cone , A, B and C are the points in the plane containing the base of the cone, while D is the point at vertex. If A, B, C and D represent flux through curved surface of cone, when a point charge Q is at points A, B, C and D respectively then
1.φ A =φC ≠0
2.φ D ≠0
3. φB = Q/2ε0
4. φA = φC = 0
 4
4Please use u're magnifier top most pt is D ; Right A ;Left C ; Centre B
 4
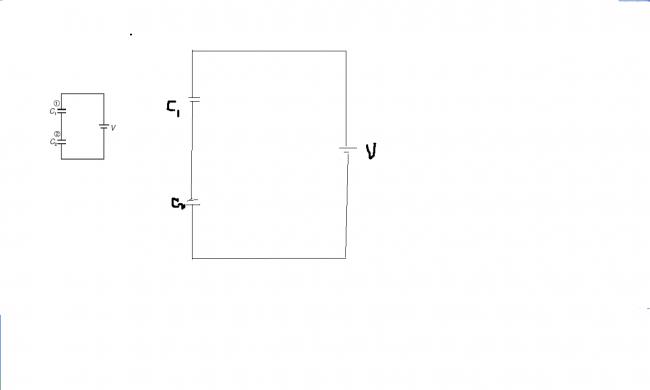
43) The circuit shown in the figure, with capacitor 1 and 2 attached in series is in steady state. Keeping the battery (of e.m.f. V) connected, now a dielectric slab is inserted into capacitor 1
1. Charge on one of the capacitor increases, while it decreases on the other
2. Potential difference across capacitor-1 decreases
3. Potential difference across capacitor-2 decreases
4. Energy stored by the system of capacitors increases
 4
44)If the cylinder were moving with constant speed v parallel to the longitudinal axis, magnetic field intensity (B) varies with distance r from the axis of the cylinder as shown by the graph

 4
45)
(!)Graphical variation of electric potential A. Linear
with distance from centre of a uniform
non-conducting solid sphere of charge
B. Parabolic
(2) Graphical variation of magnetic field
with distance from axis of a uniform solid
cylinder of current
C. Hyperbolic
(3). Path followed by a charged particle
moving in uniform electric field , D.Circular
(no other field / force is present)
E.Helical
 106
106Q2. For B imagine a second inverted cone placed with the same base as the original cone.
Total flux thru this new system = q/epsilon
So flux thru half of this is q/2epsilon (i.e. curved surface only as thru base flux becomes zero as field lines are perp. to surface)
For D, all the field lines lie parallel to the curved surface So angle between surface and field lines is 90 deg.. so flux is zero
For A and C, all the field lines that enter the conical surface also go out (except one passing thru the vertex) So net field lines remaining inside = 0
So flux of A and C = 0
 1
11>
(c)magnetic energy first gets stored in inductor and then decreases and again increases n so on
 1
13)
let intially charges on both of them Q1 and Q2
after insertion of dielectric
Q1' and Q2'
by charge conservation
Q1+Q2 =Q1'+Q2'........(1)
also potential difference remains same as battery is connected so
Q1 /C1 + Q2/C2 = Q1'/C1*K + Q2'/C2.......(2)
USING (1) AND (2) WE GET
Q1' = Q1 *{1C1-1C2} /{1C1*K-1C2}
WHICH MEANS
Q1' > Q1
HENCE CHARGE ON ONE CAPACITOR INCREASES WHILE DECREASES ON OTHER
...CONTINUED
 1
1POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE ACROSS CAPACITOR -1
V1' = Q1' / C1*K
= Q1/C1 * {C2-C1} /{C2-KC1}
V1' = V1 * (GREATER THAN 1 )
V1' >V1
SO POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE ACROSS CAPACITOR 1 INCREASES
I.E ACROSS CAPACITOR 2 DECREASES
SO OPTION (C) IS ALSO CORRECT
..CONTINUED
 4
4@taran 1991
Thanks for u're solutions
So ans for 1) c
3) is 1 2 3 4 ???
 1
1no 2 option isnt correct POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE ACROSS CAPACITOR 1 INCREASES
1 and 3 are correct
for 4th option u can check compare the energies using the formula
U= 1/2QV OR 1/2CV2 OR Q2/2C
 1
1FOR Q5
1> A AND B
COZ
E = Ïr /3ε inside
and
Q/4Ï€r2 outside
2> A and c
B= μJr /2 for r<=R
=μJ*R2 /2r for r> R
where R is radius of cylinder
3> A B C i guess accordingly as the field is applied and the intial motion of particle
D E not bcoz electric field lines dont form closed loops


