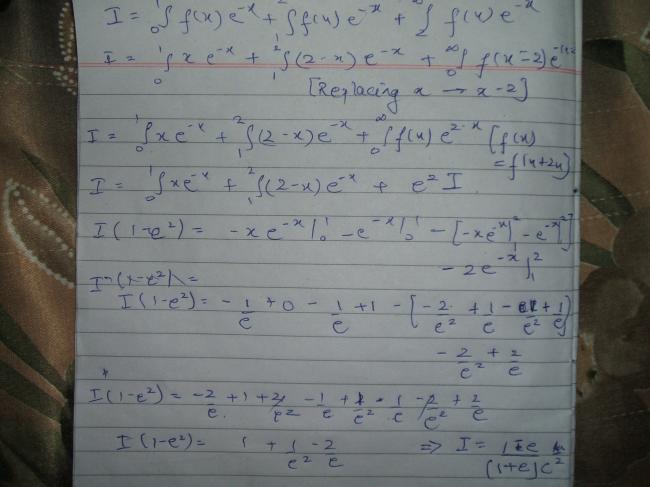mathi......i dint understand u.............and bhaiyya can u help wid tht a power -x/2 wala???
this thread is only for integration sums............
AND YA FORGOT TO TELL ALL TARGETIT USERS, I HAVE COPIED ALL THESE SUMS. SO KISIKO GAALI DENA HAIN YA KUCH KEHNA HAIN, PLEASE VISIT
http://targetiit.com/profile711.html AND POST THEM IN CHATBOX. THANKS IN ADVANCE............
1}\int_{0}^{1}e^{\sqrt{e^{x}}}\ dx+2\int_{e}^{e^{\sqrt{e}}}\ln (\ln x)\ dx
2} \int \frac{x^{3}}{(x-1)^{3}(x-2)}\ dx
3}1985 japan women university
\lim_{a\rightarrow + \infty} \frac {\int_0^a \sin ^ 4 x\ dx}{a}
4} \frac{1}{\displaystyle \int _0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \cos ^{2006}x \cdot \sin 2008 x\ dx}
5} \int_0^{\frac {\pi}{2}} \frac {x^2}{(\cos x + x\sin x)^2}\ dx
6} IF F(X)= x2 + |x| then prove that
\int_{0}^{\pi}f(\cos x)\ dx=2\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}f(\sin x)\ dx
7}Evaluate the following definite integral.
\int_{e^{2}}^{e^{3}}\frac {\ln x\cdot\ln (x\ln x)\cdot\ln\{x\ln (x\ln x)\} + \ln x + 1}{\ln x\cdot\ln (x\ln x)}\ dx
8}
Let f a nonnegative ,continuous and periodical function defined on the reals, such that the arithmetic mean of the numbers f(1), f(2),...f(n) tends to zero when n tends to infinity. Prove that f(k)=0 for any natural number k.
9}\int_{0}^{1}\frac {x\ dx}{(x^{2} + x + 1)^{\frac {3}{2}}}
10}\int_{2}^{6}\ln\frac { - 1 + \sqrt {1 + 4x}}{2}\ dx
-
UP 0 DOWN 0 23 174

174 Answers
the 23rd wala...........i cant get it.......u said to take summation.....i still cant get it
28....
I=question............partial frac
I=1/2(lnx/1+x)+lnx/(1-x))
I=1/2(I1+I2)
I1=lnxdx/1+x............by parts
I1=lnxln(1+x)-∫ln(1+x)dx/x
=lnxln(1+x)-{ln(1+x)lnx-∫lnxdx/ln(1+x)}
=lnxln(1+x)-ln(1+x)lnx+∫lnxdx/ln(1+x)
I1=0+I1..............
wat d heck am i getting.....sum1 help plzzzzzzzzzz
@nishant sir,prashant sir and manish sir
sir can u please help me with Q2
in the 2nd question on very bad but possible method is to use x-2 =t
try that.. there is a method by partial fraction, which i think will be more brilliant...
try these 2 approaches
akand see for Q23
put t=-x/2 and dt =-dx/2
∫-2atdt
=>-2∫atdt
=>-2at/loga
=>-2a-x/2/loga
@akand bhaiyya was just saying that you couldnt take that log just like that
I have been trin so hard to solve dis but all in vain , Mr. Mathie plz help me,
∫√1+x3 dx
22] first separate it:
\int \frac{1}{cos^{2}x}+\frac{2cos^{2}x}{xcos^{2}x}dx \left\{\in since \left( \right) 1+cos2x=cos^{2}x\left( \right)\ni \right\}tanx+2lnx+C
Q41.. zero?
mujhe kich pata nahiin ...
its lim(n-->∞) (1/n+1 + 1/n+2 + 1/n+3 + ... + 1/2n)
when n-->∞ all of the individual terms tend to zero..
so limit is zero.
guys wanted to tell u : nearly 60% of these sums are from www.mathlinks.ro and some are from our assignments and some from papers i solved.
as said u will find nearly 30 of these 50 posted till now from mathlinks.ro but ya, these are from pretty old threads which i solved in september that time. i am making sure, it doe not cross jee limit anywhere.
Q43.
lim(n-->∞)(summation of 2/n + 4i/n2)
= lim(n-->∞) [2/n .. n times + 4(1+2+3+...+n)/n2]
= lim(n-->∞) [(2/n).n + 4n(n+1)/2n2]
= lim(n-->∞) [2 + 2(1+1/n)]
= 2+2
= 4
Q39
put i/n=t
so 1/n=dt
it becomes 01∫cos∩/2tdt
=>2/∩sin∩/2tI01
=2/∩
Q44.
[summation of 4/n + 32i/n2 + 64i2/n3]
= 4/n .. n times + 32(1+2+3+...+n)/n2 + 64(12+22+32+..+n2)/n3
= 4 + 32.n(n+1)/2n2 + 64.n(n+1)(2n+1)/6n3
= 4 + 16 + 16/n + 64/3 + 32/n + 32/3n2
taking limit as n-->∞
we get limit = 4+16+64/3
= 124/3
Q42
put i/n->t
so 1/n->dt
it could be written as
01∫2 (2+t)5dt
=>01∫2(t5+10t4+40t3+80t2+80t+32)
now it could be easily solved by opening brackets and integrating it
@mani .. how have u used that??
put i/n =t so 1/n = dt
01∫2 (2+t)5dt
=>01∫2(t5+10t4+40t3+80t2+80t+32)
is there any such rule for that?
this is a method known as limit of sum
it is used to find summations using integrations
if u have any book of integeration
find the topic integeration as limit of a sum
for more knowledge
this year paper contained question of limit as a sum
try doing Q43.. using that method mani.. i think ull get different answer...