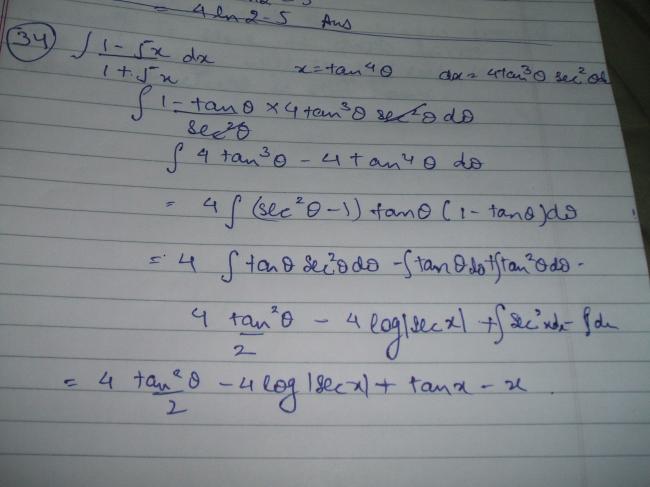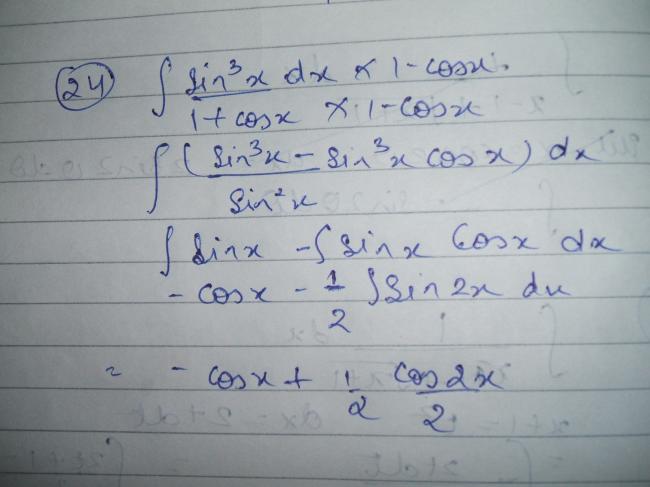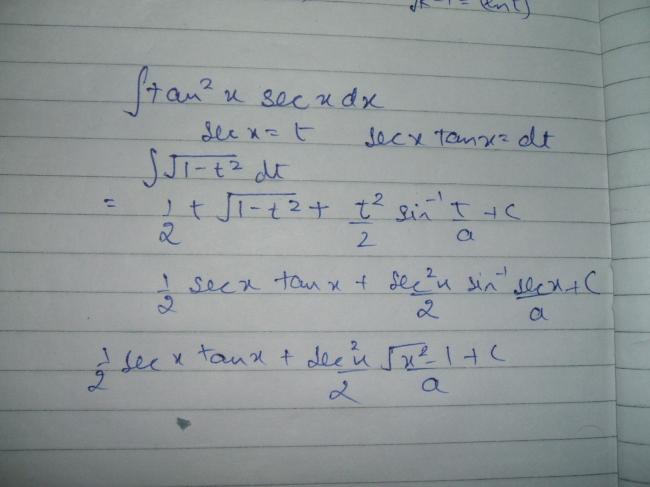this thread is only for integration sums............
AND YA FORGOT TO TELL ALL TARGETIT USERS, I HAVE COPIED ALL THESE SUMS. SO KISIKO GAALI DENA HAIN YA KUCH KEHNA HAIN, PLEASE VISIT
http://targetiit.com/profile711.html AND POST THEM IN CHATBOX. THANKS IN ADVANCE............
1}\int_{0}^{1}e^{\sqrt{e^{x}}}\ dx+2\int_{e}^{e^{\sqrt{e}}}\ln (\ln x)\ dx
2} \int \frac{x^{3}}{(x-1)^{3}(x-2)}\ dx
3}1985 japan women university
\lim_{a\rightarrow + \infty} \frac {\int_0^a \sin ^ 4 x\ dx}{a}
4} \frac{1}{\displaystyle \int _0^{\frac{\pi}{2}} \cos ^{2006}x \cdot \sin 2008 x\ dx}
5} \int_0^{\frac {\pi}{2}} \frac {x^2}{(\cos x + x\sin x)^2}\ dx
6} IF F(X)= x2 + |x| then prove that
\int_{0}^{\pi}f(\cos x)\ dx=2\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}f(\sin x)\ dx
7}Evaluate the following definite integral.
\int_{e^{2}}^{e^{3}}\frac {\ln x\cdot\ln (x\ln x)\cdot\ln\{x\ln (x\ln x)\} + \ln x + 1}{\ln x\cdot\ln (x\ln x)}\ dx
8}
Let f a nonnegative ,continuous and periodical function defined on the reals, such that the arithmetic mean of the numbers f(1), f(2),...f(n) tends to zero when n tends to infinity. Prove that f(k)=0 for any natural number k.
9}\int_{0}^{1}\frac {x\ dx}{(x^{2} + x + 1)^{\frac {3}{2}}}
10}\int_{2}^{6}\ln\frac { - 1 + \sqrt {1 + 4x}}{2}\ dx
-
UP 0 DOWN 0 23 174

174 Answers
:D
hey dude isko bhi integrate karo
∫ (√x-3 ) ( sin-1(ln(x) ) + cos-1(ln(x) ))
...post:65 and mani's reply in post:66..
___________________________________
:D
post:91
_______________________
that was another trap from grandmaster...
The given function...
√x-3 so x≥3
but then sin-1(lnx) and cos-1(lnx) doesn't exist....
:D
:D
:D
so how can we take... sin-1(lnx)+cos-1(lnx)=Ï€/2..
:D
______________________________
Grandmaster always makes trap... ('SP Sir' ke nakshe kadam par hai....)
yeh sp sir kaun hai?????
and bye the way
sin-1(lnx)+cos-1(lnx)=Ï€/2..
is this false[7]
@priyam my teachers r incomplete[3]
please tell the way to make them complete[3]
are mere kahne ka matlab...
he is the most teacher like teacher.. i have ever seen...
@manipal singh
arre check karke dekho the function doesnot exists,so how can its anti derivative be??
51]\int {\frac{{x^3 + 1}}{{x(x^3 - 8)}}} dx
52]\int \frac{1} {x\sqrt{25x^2+16}}
53]\int_{0}^{\infty} x e^{-x^2} dx
54]\int^{\infty}_0 x / ( e^x - 1) \ dx
55]\int^{\infty}_0 x^2 / ( e^x - 1) \ dx
hey mani d q wich i posted u did gt that wrng
c u hav taken ex=t
so lnt=x
nw in d q d deno is( (lnx)^2+1 )^2
bt u hav missed d (lnx)^2 instead u hav taken lnx
56]\int {(x^2 + 2x + 2)e^{ - x} } dx
57]\int^a_0 \frac{f(x)}{f(x) + f(a-x)}dx
answer in terms of `a`
58]lim B\to\infty [I(a)] = \int_\frac{1}{B}^1(t^{-1/2}e^{-a(t+t^{-1})})dt + \int_1^B(t^{-1/2}e^{-a(t+t^{-1})})dt
59]\int\limits_0^2 {x^3 \sqrt{1 - x^2 } dx}
60]\displaystyle \int \tan^2 x \sec x \ dx
61]\int \frac{(b-a)dx} {x[ln^2x - (a+b)lnx+ab]}
63]\int\ \sqrt{tanx}-\sqrt{cotx}dx
by A single substitution
64]\displaystyle\frac{1}{\ln (\pi)}\int_{\frac{-\pi}{7}}^{\frac{\pi}{7}}\tan \left(x^{41}+\frac{1}{\pi}x^5-x^3+x\right)dx
from a old calculus book
65]\int_{-1}^1 \frac{\sqrt{1-x^2}}{a-x}\ dx\ (a>1)
66] prove for x≥0 ,
\int_{0}^{x}(t-t^{2})\sin^{2004}t\ dt <\frac{1}{2006}
67] For t>0, find the minimum value of
\int_{0}^{1}x|e^{-x^{2}}-t| dx.
68]Given the parabola:y=x2 If the circle centered at y axis with radius 1 has common tangent lines with C at distinct two points, then find the coordinate of the center of the circle K and the area of the figure surrounded by C and K.
69]\int^{\pi}_{0}{x^{2}\sin^{2}x}\,dx
70]\lim_{t\rightarrow 0}\int_{0}^{2\pi}\frac{|\sin (x+t)-\sin x|\ dx}{|t|}.
71] FIND THE NUMBER OF REAL ROOTS OF THIS QUADRATIC
x^{2}=-2x+k+\int_{0}^{1}|t+k|\ dt.
72] find `a` such that
\int_{0}^\frac{\pi}{2}(\sin x+a\cos x)^{3}\ dx-\frac{4a}{\pi-2}\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}x\cos x dx=2.
73] Find the continuous function f(x) and constant number such that
\int_{0}^{x}f(t)\ dt=e^{x}-ae^{2x}\int_{0}^{1}f(t)e^{-t}\ dt.
74] \lim_{n\to\infty}n\int_{-1}^{1}e^{-n|a-x|}\ dx.
where a is a real number
75] prove that \int_{-\pi}^{\pi}\cos(2x)\cos(3x)\cos(4x)...\cos(2005x)dx >0
FOR
Q67
http://targetiit.com/iit_jee_forum/posts/graph_bana_ke_dikhao_3607.html
63)
wrtie tanx and cot x in form of sinx n cosx
then u get num as(sinx-cosx) n den as root sin2x
write sin2x as
(sinx+cosx)2 -1
take sinx +cosx =t
(cosx-sinx )dx =dt
then adjsut d num n egt d ansewr